Discovering the Depths: A Comprehensive Overview to Concrete Scanning and Its Diverse Applications
In the world of construction and facilities advancement, the thorough process of concrete scanning holds an essential duty in ensuring the structural stability and security of tasks. As innovation proceeds to progress, the applications of concrete scanning have expanded far past mere surface-level assessments.
Significance of Concrete Scanning
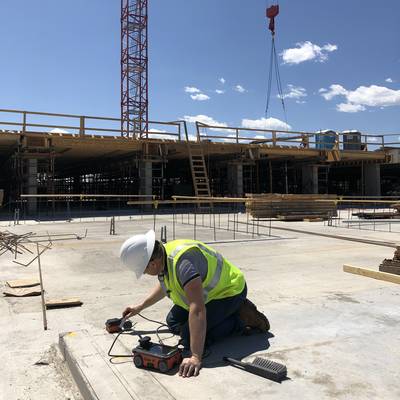
Understanding the significance of concrete scanning is important in guaranteeing the security and honesty of frameworks during building and construction and remodelling tasks. Concrete scanning uses advanced innovations such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction to detect ingrained items, voids, or other anomalies within concrete frameworks - RainierGPR Concrete Scanning. By performing detailed scans prior to boring, reducing, or coring right into concrete, construction groups can prevent unexpected damage to important structural aspects like rebar, conduits, or post-tension cords. This aggressive technique not only prevents pricey repair services and job delays but also enhances total construction safety and security by reducing the danger of architectural failures or collapses because of endangered stability.
Furthermore, concrete scanning plays a pivotal duty in making sure conformity with building regulations and laws that mandate the defense of existing structural elements throughout construction tasks. By precisely mapping out the interior composition of concrete, scanning innovations allow building and construction experts to make educated decisions that maintain the architectural stability and sturdiness of structures and framework tasks. Basically, the value of concrete scanning hinges on its capacity to safeguard both the structural integrity and the personnel associated with building and construction undertakings.
Technologies Used in Concrete Scanning
Concrete scanning relies on sophisticated modern technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electromagnetic induction to precisely identify ingrained objects and anomalies within concrete structures. Ground-penetrating radar operates by giving off high-frequency electro-magnetic waves right into the concrete.
Electro-magnetic induction, on the other hand, works by creating magnetic fields around a concrete structure through a transmitter coil. When steel items exist within the concrete, they disrupt these magnetic fields, creating eddy currents to flow with the metal. By gauging the changes in the magnetic fields with a receiver coil, the system can determine the place of metal items in the concrete.
These advanced modern technologies play an essential duty in non-destructive screening, making sure the security and integrity of concrete frameworks in numerous markets.
Applications in Building Industry
Within the building industry, concrete scanning modern technology locates varied applications that boost project performance and safety. One crucial application is the detection of rebar, post-tension cable televisions, and various other embedded items prior to drilling or reducing into concrete structures. By properly drawing up these aspects, construction teams can avoid pricey problems, make sure structural stability, and avoid prospective safety dangers. Furthermore, concrete scanning is made use of for finding gaps, such as air pockets or areas of wear and tear within concrete, which can jeopardize the general toughness of a structure. By identifying these spaces beforehand, construction professionals can take required steps to address them and maintain the toughness of the structure. Moreover, concrete scanning plays an important function in quality assurance by verifying the thickness of concrete covers over reinforcement, ensuring conformity with layout requirements and criteria. In general, the applications of concrete scanning in the building and construction sector contribute considerably to streamlining project operations, reducing threats, and delivering top notch results.
Security Advantages of Concrete Scanning
In the realm of construction security, the application of concrete scanning technology provides a critical benefit in preemptively identifying potential threats and strengthening architectural integrity. By using sophisticated scanning approaches such look at here now as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction, construction teams can precisely locate rebar, post-tension cables, channels, and other covert items within concrete frameworks. This proactive technique substantially decreases the threat of unexpected strikes during exploration, reducing, or coring activities, thereby protecting against costly problems, injuries, and task delays.
Furthermore, concrete scanning improves worker safety and security by supplying real-time information concerning the architectural problem of concrete aspects. By resolving prospective security problems without delay, concrete scanning adds to producing a secure functioning setting and alleviating the probability of structural failings or mishaps on construction websites.
Future Patterns in Concrete Scanning
Emerging improvements in scanning modern technology are positioned to revolutionize the field of concrete assessment and evaluation. By taking advantage of the power of AI, these systems can examine large quantities of information accumulated throughout scanning processes to offer more precise and thorough understandings right into the condition of concrete frameworks.
Another considerable fad is the development of even more straightforward and portable scanning devices. Miniaturization of scanning tools enables much easier access to confined spaces and remote locations, making inspections a lot more efficient and comprehensive. In addition, advancements in cordless interaction technologies visit homepage make it possible for real-time information transfer and analysis, facilitating quicker decision-making procedures.
Moreover, there is an expanding concentrate on sustainability in concrete scanning technologies - RainierGPR Concrete Scanning. Manufacturers are increasingly integrating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient functions right into their devices to reduce environmental effect. These future patterns are established to boost the effectiveness, accuracy, and sustainability of concrete scanning methods, forming the sector's future landscape
Conclusion
Finally, concrete scanning plays an important duty in the building and construction industry by making sure the safety and performance of different jobs. By utilizing innovative innovations, such as GPR and radar imaging, professionals are able to properly discover possible dangers within concrete structures. The applications of concrete scanning are huge and continue to progress, making it a necessary tool for preserving the integrity of buildings and framework. As modern technology developments, the future of concrete scanning holds promising growths for enhancing building and construction procedures.
